Google Scholar | Biography
The role protein phosphorylation and ubiquitylation in human health and disease
The protein kinase ALPK1 and human disease
The protein kinase ALPK1 is normally activated by nucleotide heptoses (ADP-heptose, UDP-heptose and CDP-heptose) produced by bacteria and some viral and fungal pathogens, but not by human cells. The nucleotide heptoses bind to the N-terminal domain of ALPK1 initiating conformational changes that activates the kinase and permits it to phosphorylate the adaptor protein TIFA. This causes TIFA to polymerise into TIFAsomes, and trigger a signal transduction pathway that leads to the production of inflammatory mediators to combate microbial infection [1, 2] (Figure 1).
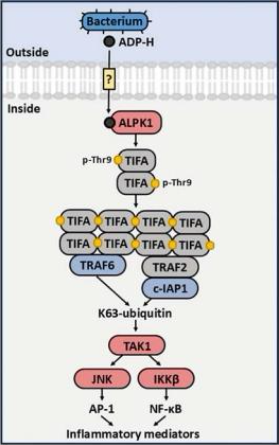
ALPK1 signalling pathway
Human variation in ALPK1 causes two human diseases, termed ROSAH syndrome and spiradenoma. The mutation of Thr237 to Met [3] or Ser277 to Phe [4] cause ROSAH syndrome (Retinal dystrophy, Optic nerve oedema, Splenomegaly, Anhidrosis (the inability to sweat) and Headache) an autosomal dominant disease that leads to blindness by the age of 20-40. In contrast, spiradenomas are a group of predominantly benign neoplasms, usually observed as abnormal growths on the head, neck and upper body, which can undergo malignant transformation to Spiradenocarcinomas with high rates of mortality. 35-40% of patients with spiradenoma or spiradenocarcinoma have the same Val1092 to Ala mutation located in the protein kinase domain of ALPK1 [3].
We recently discovered that the human variants of ALPK1 leading to either ROSAH syndrome or spiradenoma/spiradenocarcinoma cause the protein kinase to lose its specificity for nucleotide heptoses, and to also be activated by nucleotide-hexoses and nucleotide-pentoses present in human cells, namely UDP-mannose, GDP-mannose and ADP-ribose [3, 4]. Consequently, the disease-causing mutations cause chronic activation of the ALPK1-TIFA pathway without microbial infection and hence lead to disease. These may be the first diseases caused by loss of the specificity of an enzyme for its allosteric activator.
We are continuing our research to elucidate poorly understood aspects of the ALPK1-TIFA pathway, to develop and study mouse models of the disease, and to identify compounds that inhibit the disease causing variants of ALPK1 selectively.
Sugar ubiquitylation; a new surveillance mechanism for the recognition and elimination of unbranched glycogen
Ubiquitylation was discovered over 40 years ago as a mechanism that marks proteins for destruction. Since then, ubiquitylation has been found to regulate the functions of proteins in other ways, but the concept that proteins are the sole targets for ubiquitylation has never altered. Now our lab has found that sugars can also be ubiquitylated.
We discovered that mice expressing an E3-ligase inactive mutant of HOIL-1 instead of wild type HOIL1, accumulate insoluble deposits in the brain, heart and other tissues, termed Polyglucosan Bodies (PB) [5]. PB comprise unbranched glycogen lacking the alpha1:6 branch points found in normal glycogen. The gradual accumulation of PB with age leads to cardiomyopathy and heart failure and/or to fatal neurological conditions.
We also found that the HOIL-1 is a very unusual E3 ligase, which catalyses the formation of ester bonds between the C-terminal carboxylate of ubiquitin and the hydroxyl side chains of serine and threonine residues in proteins [6, 7] (Figure 2)
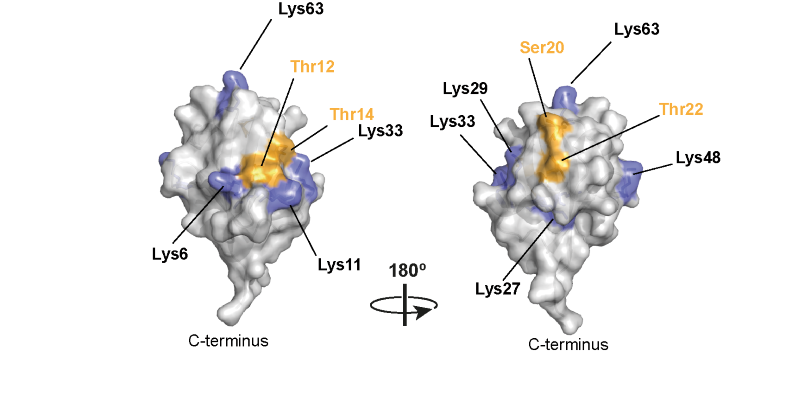
We then found that HOIL-1 can ubiquitylate the C6 hydroxyl group of glucose in unbranched glucosaccharides, the hydroxyl group at which alpha 1:6 glucosidic linkages (branch points) are formed. This observation led us to propose that HOIL-1 ubiquitylates unbranched glycogen molecules, formed by errors of metabolism, leading to their uptake into lysosomes where they are hydrolysed by the lysosomal acid alpha1:4 glucosidase [5].
Excitingly, we have now been able to establish that unbranched glycogen molecules are indeed polyubiquitylated in human cells and are now investigating which other E3 ligases contribute to the formation of these polyubiquitin chains. We are also studying how ubiquitylated unbranched glycogen enters lysosomes. Our research is opening up new aspects of ubiquitin biology.
Recent Publications
- Snelling, T., Shpiro, N., Gourlay, R., Lamoliatte, F. and Cohen, P.(2022)“Coordinated control of the ADP-heptose/ALPK1 signalling network by the E3 ligases TRAF6, TRAF2/c-IAP1 and LUBAC” Biochem J. 479, 2195-2216. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20220401
- Cohen, P. and Snelling, T. (2025) “Diseases caused by altered specificity of a protein kinase for its allosteric activators.” Trends Biochem Sci 50, 61-70 https://www.cell.com/trends/biochemical-sciences/pdf/S0968-0004(24)00233-0.pdf
- Snelling, T., Saalfrank, A., Wood, N. and Cohen, P. (2023) ALPK1 mutants causing ROSAH syndrome or Spiradenoma are activated by human nucleotide sugars. Proc.Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2313148120 https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2313148120
- Snelling, T., Garnotel, L.O., Jeru, I., Tusseau, M., Cuisset, L., Perlat, A., Minard, G., Benquey, T., Maucourant, Y., Wood, N.T., Cohen, P. and Ziegler, A. (2024) Discovery and Functional analysis of a novel ALPK1 variant in ROSAH syndrome. Open Biology 14 https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsob.240260
- Kelsall, I.R., McCrory, E.H., Xu, Y., Scudamore, C.L., Nanda S.K., Mancebo-Gamella, P., Wood N.T., Knebel, A., Matthews, S.J. and Cohen, P. (2022) “HOIL-1 ubiquitin ligase activity targets unbranched unbranched glucosaccharides and is required to prevent polyglucosan accumulation”EMBO Journal 41:e109700 https://www.embopress.org/doi/pdf/10.15252/embj.2021109700
- Kelsall, I.R., Zhang, J., Knebel, A., Arthur, J.S.C. and Cohen, P. (2019) ‘The E3 ligase HOIL-1 catalyses ester bond formation between ubiquitin and components of the myddosome in mammalian cells.” Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 116, 13293-13298 https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1905873116
- McCrory, E., Akimov, V., Cohen, P.* and Blagoev, B.* (2022) “ Identification of ester-linked ubiquitylation sites during TLR7 signalling increases the number of inter-ubiquitin linkages from 8 to 12” Biochem J. 479, 2419-2431 * joint corresponding authors. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20220510
Review
Cohen, P., Cross, D. and Janne, P.A. (2021) “Kinase Drug Discovery 20 years after Imatinib: progress and future directions. Nat. Rev. Drug Disc. 20, 551-569 10.1038/s41573-021-00195-4


